Understanding Computational Requirements of
Preservation and Reconstruction
Simulation Environment for Understanding Computational Requirements of Preservation and Reconstruction
We focused on evaluating the information value, data volumes and computational requirements during decision making processes when preservation is our main objective.
The problem is stated as information gathering about decision processes using geospatial electronic records and described in more details below. Our work addresses the tradeoffs of electronic information preservation in terms of file format, data volumes and computational requirements. We have evaluated storage and retrieval efficiency of boundary data representations for LLS, TIGER and DLG data structures. Next, we focused on evaluating the information value, data volumes and computational requirements during decision making processes when preservation is our main objective. The problem is stated as information gathering about decision processes using geospatial electronic records and described in more details below.
The government makes a large number of high-confidence decisions using geospatial electronic records. Decision makers might process maps and photographs called raster data, vector data that represent linear features like county boundaries or streams, and statistics in tabular form to arrive to a decision that affects the lives of many citizens. The problem is to document, preserve, and reconstruct the processes later, often years after the initial decision has been made.
While any government decision process is complicated on its own, tracking the analysis of geospatial electronic records supporting government decisions adds another layer of complexity. We must understand the cost of information preservation and the value of preserved information. A team from the National Center for Supercomputing Applications works with the National Archives and Records Administration to provide software tool (Image Provenance to Learn - IP2Learn) for:
- simulating complicated high-confidence decision scenarios,
- preserving the gathered information in temporally sustainable data containers, and
- reconstructing high-assurance decision making processes.
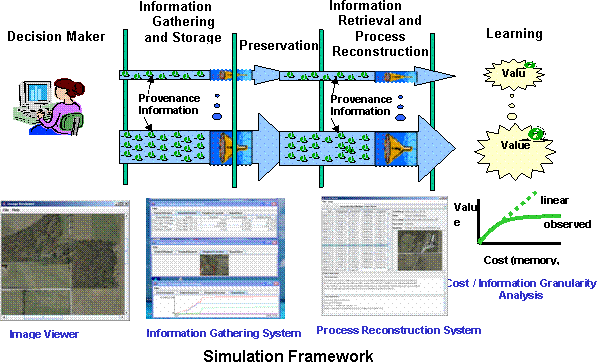
IP2Learn is a simulation framework for studying temporal aspects of data processing in the context of high assurance decision making and high confidence application scenarios. IP2Learn focuses on decision processes based on examining images, tracking all operations by a user during image inspection and reconstructing the image based decision process by using multiple variable settings. It allows archivists, for instance, to examine empirically the tradeoffs related to the questions: what should be preserved; how should the data be gathered, stored, and retrieved; how should the decision-making processes be reproduced; and what questions will researchers be able to answer using the reproduced information. The prototype can record and reproduce information about how a digital image is manipulated (e.g., select, crop, magnify, or adjust the color of an image) at varying levels of detail - from a textual summary of the actions taken to a full video replay of the actions taken in inspecting an individual image. IP2Learn also captures, summarizes and displays information about the costs (storage space and computing cycles) associated with each approach to capturing, preserving, and providing access to these records. We envision the use of IP2Learn for not only evaluations of cost versus information granularity tradeoffs of information gathering but also for auditing and quality control purposes as well as for education and training purposes.
Using IP2Learn we have been conducting trade-off studies related to encryption, compression, storage file format, information gathering mechanisms and meta-data organization. We have also expanded the simlation framework by semi-automated generation of reports documenting the decission processes.
For additional context of this research, please, visit the ERA research web site at
http://www.archives.gov/era/research/research-publications.html and specifically the IP2Learn description at http://www.archives.gov/era/research/image-provenance-to-learn.html
Team members
- Sang-Chul Lee
ISDA, NCSA, University of Illinois - Rob Kooper
ISDA, NCSA, University of Illinois - Peter Bajcsy
Research group ISDA, National Center for Supercomputing Applications, University of Illinois
- S-C Lee and P. Bajcsy, "Understanding Challenges in Preserving and Reconstructing Computer-Assisted Medical Decision Processes.", Workshop on Machine Learning in Biomedicine and Bioinformatics (MLBB07) of the 2007 International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA'07) December 13-15, 2007, Cincinnati, Ohio, oral presentations [pdf 1.1MB]
- P. Bajcsy, "Challenges in Preserving and Reconstructing Computer Assisted Processes," Society of American Archivists, Chicago, August 2007 (oral presentation) [pdf 2.8MB]
- P. Bajcsy, "Data Processing and Analysis.", Chapter IV (pp. 258-378) of the book Hydroinformatics: Data Integrative Approaches in Computation, Analysis, and Modeling, eds. P. Kumar, J. Alameda, P. Bajcsy, M. Folk and M. Markus, vol. 2, p534, CRC Press LLC 2006. [book cover jpg] [content pdf 26kB]
This research was supported by a National Archive and Records Administration (NARA) supplement to NSF PACI cooperative agreement CA SCI-9619019. We also acknowledge NCSA/UIUC.