
 University of Illinois
University of Illinoisat Urbana-Champaign

|
About
Conversion Software Registry (CSR)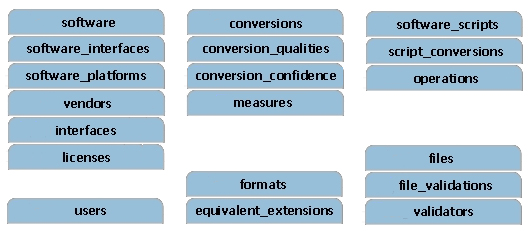
Figure 1. The CSR pseudo-tables block design. The CSR includes information about software, file formats, software scripts and quantitative conversion measures, as well as the information about test files. Conversion Software Registry (CSR) has been designed for collecting information about software packages that are capable of file format conversions. The work is motivated by a community need for finding file format conversions inaccessible via current search engines and by the specific need to support systems that could actually perform conversions, such as the NCSA Polyglot. In addition, the value of CSR is in complementing the existing file format registries and introducing software quality information obtained by content-based comparisons of files before and after conversions. The contribution of this work is in the CSR data model design that includes file format extension based conversion, as well as software scripts, software quality measures and test file specific information for evaluating software quality. The CSR system serves as the source of information and a test bed for the system that can execute the conversions automatically by using the third party software, for example, NCSA Polyglot. The CSR system is a database with a web-based interface that provides services related to a) finding a conversion path between formats b) uploading information about the 3rd party software packages and file extensions, c) uploading files for testing, and finally d) uploading scripts in operating system (OS) specific scripting languages (Windows AutoHotKey, AppleScript and Perl) for automated conversions according to the idea of imposed code reuse used by NCSA Polyglot. In order to provide file format conversion services, we have included the following components into CSR related to software capable of conversions: input and output file formats (extensions), scripts operating on the software, validated files to be used for information loss measurements, as well as quantitative measures of the information loss for conversions. These components define the data entities of the CSR database as illustrated in Figure 2. 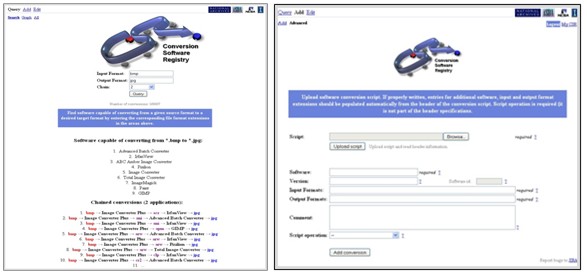
Figure 2. Left: The CSR web interface showing a conversion query to find the shortest conversion path between the two formats entered. The single and multiple path conversions are listed alphabetically. Right: The front end of the 'Add->Script' pane of the Conversion software registry web interface.. The CSR focuses: on software and finding the format conversion paths described by a number of software packages and unique input and output formats. The formats themselves are represented by extensions. While not always unique, extensions are often the only accessible information when the 3rd party software is installed (often listed under the File/Open menu in most packages). The CSR also contains information about the software, operating system, software interface and scripts to execute the software. The scripts are important for the automating conversions with the 3rd party software and can be implemented using AutoHotkey scripts (Windows), AppleScript (Mac) or one of a variety of scripting languages for Unix. The information loss due to file format conversions is measured externally by different techniques within the NCSA object-to-object comparison framework called Versus. The comparison is relevant to the software domain, for example for 3D applications surface area or spin images are used and the loss (0-100 range with 100 representing no loss) for a particular software-conversion pair is stored in the database. The information loss also represents edge weights to Input/Output (I/O) Graph, a simple workflow used for finding the shortest conversion path. The CSR is written as a web service. It consists of three main components: Query, Add, Edit. In the Query mode users can a) view list of all software packages with their conversion options, b) select subsets of software in the I/O-Graph, c) search the database by conversions (see Figure 2 left), software, extensions, MIME and PUID. The I/O-Graph contains all information about installed applications and the conversions they allow. The JAVA applet front end is part of the CSR web visualization interface. Section Add allows users to add new software packages with their conversion capabilities and upload the software scripts to automate them (Figure 2 right). The last section, Edit is designed for adding detailed information about the software, extensions and for uploading the test files. CSR requires users to login for adding and editing. The web fields are auto completed to help search. CSR url: http://isda.ncsa.uiuc.edu/NARA/CSR/People,
Publications, Presentations
AcknowledgementThis research was partially supported by a National Archive and Records Administration (NARA) supplement to NSF PACI cooperative agreement CA #SCI-9619019. Team members
Publications and presentations
|
Navigation
|

