University of Illinois
University of Illinoisat Urbana-Champaign

|
About
Understanding Preservation and Reconstruction of Electronic RecordsThe management and appraisal of electronic documents have been identified among the top ten challenges in the 34th Semi-annual Report to Congres by National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) Office of Inspector General (OIG) in 2005, and in the Strategic Plan of the National Archives and Records Administration 2006-2016: Preserving the Past to Protect Future. Our research is motivated mainly by the NARA Strategic Plan and the NARA 1441 directive specifically addressing document appraisal criteria. As stated in the Appraisal Policy of NARA: Not all records that constitute essential evidence possess archival value. It is through the appraisal process that NARA determines the value and thus the final action (disposition) of Federal records that are no longer needed for current Government business. The objective of our project research is to define and improve specific decisions with which Electronic Records Archives (ERA) appraises electronic holdings. The approach includes:
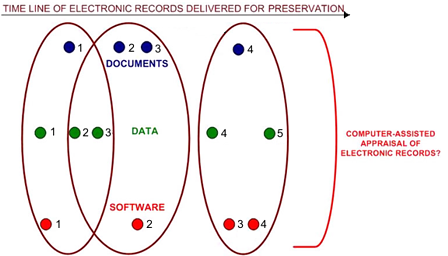
Overview of temporal aspects of electronic records delivered for preservation. The new record (document '4', data '4' and '5' and software '3' and '4') is automatically evaluated and related to other, already cathegorized records. Our goal is to provide computer assisted support for
answering several appraisal criteria such as: Are the records
related to other permanent records?, What is the timeframe covered
by the information?, What is the volume of records?, Is sampling an
appropriate appraisal tool?
The studies above focus on automated extraction of relationship among documents (metadata extraction), integrity verification and document versions sampling. Additionally we would like to generate and retrieve information about temporal relationships among documents (data and software) categories. AcknowledgmentsThe project is supported by the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA). Projects
description
Exploratory Document Appraisal Framework.The volume of contemporary documents and the number embedded object types is steadily growing. There is a lack of understanding how to compare documents containing heterogeneous digital objects and what hardware and software configurations would be cost-efficient for handling document related operations such as appraisals. The project addresses the problems of image/text/vector graphics extraction from PDF documents, computation of image/text/vector graphics characterictics, fusion of similarity metrics computed for all PDF components, grouping of documents, integrity verifications, and sampling. Aditionally we perform counting operations using cluster computing and the Map and Reduce programming paradigm. 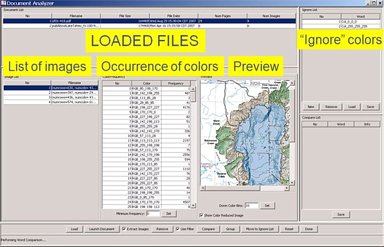
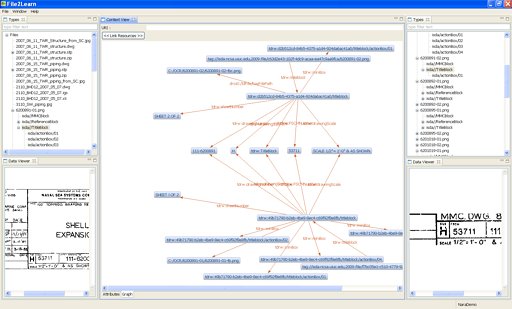
PDF content is shown in the developed framework, Document To Learn (Doc2learn). Here image primitves are described as groups of colors. The figure shows multiple views of the PDF content as needed for appraisal. While the PDF reader would present the view of the document layout per page, other views might be needed for understanding the characteristics of PDF components. 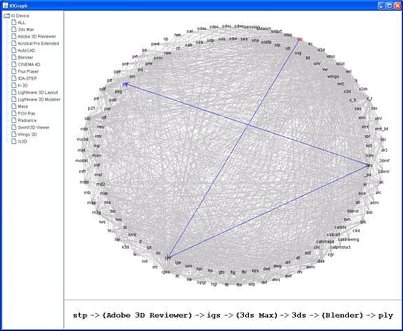
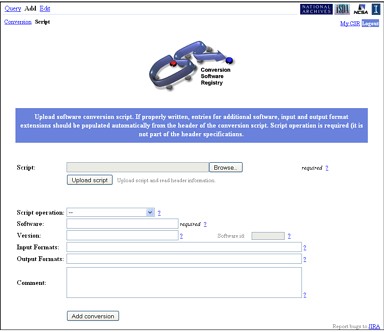
IOGraph: An illustration of how the IOGraph tool is used for finding the shortest conversion sequence from an original 3D file format (stp) to a target 3D file format (ply). File format conversions.Motivated by the large number of file formats within the 3D file domain, NCSA Polyglot was created to provide an extensible, scalable, and quantifiable means of converting between formats. The system is extensibile in terms of being able to easily incorporate new conversion software, scalable in being able to distribulte work load among parrallel machines, and quantifiable in having a built in framework for measuring information loss across conversions. The tool called IOGraph (left) could provide information about the shortest conversion path from a source file format to a target format. Around 140 file formats for 3D data and 17 software packages with import/export and 3D display functionalities are supported. Conversion
Software Registry (CSR)
|
Navigation
|